做音乐网站建设的开发平台深圳优化怎么做搜索
PMPP char3 – Multidimensional grids and data
五一过后,有些工作要赶,抽出时间更新一下。这一章基本都熟练掌握,在做习题过程中有一些思考。这里涉及到了一点点GEMM(矩阵乘),GEMM有太多可深挖的了,推荐一篇博客How to Optimize a CUDA Matmul Kernel for cuBLAS-like Performance: a Worklog (siboehm.com)。另外,我还发现上一篇博客,有写错的地方,这篇博客的末尾做了一下勘误。这里记录我的个人理解,有不正确的地方,欢迎留言或者私信讨论。
课后习题
- In this chapter we implemented a matrix multiplication kernel that has each
thread produce one output matrix element. In this question, you will
implement different matrix-matrix multiplication kernels and compare them.
a. Write a kernel that has each thread produce one output matrix row. Fill in
the execution configuration parameters for the design.
b. Write a kernel that has each thread produce one output matrix column. Fill
in the execution configuration parameters for the design.
c. Analyze the pros and cons of each of the two kernel designs.
答案:
a 部分 (来自大模型)
__global__ void matrixMulRow(float *A, float *B, float *C, int m, int n, int k) {int row = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;if (row < m) {for (int col = 0; col < k; ++col) {float sum = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {sum += A[row * n + i] * B[i * k + col];}C[row * k + col] = sum;}}
}
dim3 threadsPerBlock(1, 256);
dim3 blocksPerGrid(1, (m + threadsPerBlock.y - 1) / threadsPerBlock.y);
matrixMulRow<<<blocksPerGrid, threadsPerBlock>>>(A, B, C, m, n, k);
b部分 (来自大模型)
__global__ void matrixMulCol(float *A, float *B, float *C, int m, int n, int k) {int col = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;if (col < k) {for (int row = 0; row < m; ++row) {float sum = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {sum += A[row * n + i] * B[i * k + col];}C[row * k + col] = sum;}}
}
dim3 threadsPerBlock(256, 1);
dim3 blocksPerGrid((k + threadsPerBlock.x - 1) / threadsPerBlock.x, 1);
matrixMulCol<<<blocksPerGrid, threadsPerBlock>>>(A, B, C, m, n, k);
c部分
假设A、B、C都是行主序;这里也不使用共享内存。一次读入一个缓存行,访问一行数据的话,存在访存局部性,需要用到的数据就在缓存中;访问一列数据的话,不存在访存局部性,需要用到的数据就不在缓存中,需要再读一个缓存行。假设一个缓存行时64B,对应16个float32。
| 访问A | 访问B | 访问C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 一个线程处理C中的一行 | 连续访问,只访问一行。访存次数=K/16 | 不连续访问,一次访问一列,访存次数=K;总共要访问N列,访问次数=N*K | 连续访问,只访问一行。访存次数=K/16 |
| 一个线程处理C中的一列 | 不连续访问,只访问一列。访存次数=M | 不连续访问,一次访问一列,访存次数=K;总共要访问N列,访问次数=N*K | 不连续访问,只访问一列。访存次数=M |
如果访存数据量较小,也就是a那种,可以直接放到寄存器中,这样访存cycle更短。
如果访存数据量较大,reg的容量就不够用,需要一部分存到L1上面,甚至L1也装不下,要从global里读取。涉及多个存储数据一致性、data hazard的问题,效率就很低。
- A matrix-vector multiplication takes an input matrix B and a vector C and
produces one output vector A. Each element of the output vector A is the dot
product of one row of the input matrix B and C, that is, A[i] = ΣB[i][j] * C[j].
For simplicity we will handle only square matrices whose elements are single-
precision floating-point numbers. Write a matrix-vector multiplication kernel and
the host stub function that can be called with four parameters: pointer to the output
matrix, pointer to the input matrix, pointer to the input vector, and the number of
elements in each dimension. Use one thread to calculate an output vector element.
答案:
其实,这道题就是参考gemm,实现gemv。就是把输出C的一个变量(C[i])映射到一个线程上,这个线程遍历j个变量,再各自点乘+求和(也就是j维度上做规约)。
以下是大模型写出来的程序,我看了下没啥问题,测试了下也是ok的。输入为A和B,输出为C。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <random>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>#define CHECK(call) \
{ \const cudaError_t error = call; \if (error != cudaSuccess) { \std::cout << "Error: " << __FILE__ << ":" << __LINE__ << ", " << cudaGetErrorString(error) << std::endl; \exit(1); \} \
}__global__ void matrixVectorMultiply(const float* A, const float* B, float* C, int rows, int cols) {int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;if (i < rows) {float sum = 0.0f;for (int j = 0; j < cols; ++j) {sum += A[j] * B[i * cols + j];}C[i] = sum;}
}int main() {int rows = 1024;int cols = 768;std::vector<float> hostA(cols);std::vector<float> hostB(rows * cols);std::vector<float> hostC(rows);std::vector<float> resultC(rows);// 初始化输入数据std::random_device rd;std::mt19937 gen(rd());std::uniform_real_distribution<float> dis(-1.0, 1.0);for (int j = 0; j < cols; ++j) {hostA[j] = dis(gen);}for (int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {for (int j = 0; j < cols; ++j) {hostB[i * cols + j] = dis(gen);}}// 分配设备内存float* deviceA;float* deviceB;float* deviceC;CHECK(cudaMalloc(&deviceA, cols * sizeof(float)));CHECK(cudaMalloc(&deviceB, rows * cols * sizeof(float)));CHECK(cudaMalloc(&deviceC, rows * sizeof(float)));// 将输入数据从主机复制到设备CHECK(cudaMemcpy(deviceA, hostA.data(), cols * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice));CHECK(cudaMemcpy(deviceB, hostB.data(), rows * cols * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice));// 启动内核int threadsPerBlock = 256;int blocksPerGrid = (rows + threadsPerBlock - 1) / threadsPerBlock;matrixVectorMultiply<<<blocksPerGrid, threadsPerBlock>>>(deviceA, deviceB, deviceC, rows, cols);CHECK(cudaGetLastError());// 将输出数据从设备复制到主机CHECK(cudaMemcpy(hostC.data(), deviceC, rows * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost));// 验证结果正确性for (int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {float sum = 0.0f;for (int j = 0; j < cols; ++j) {sum += hostA[j] * hostB[i * cols + j];}resultC[i] = sum;}for (int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {if (std::abs(hostC[i] - resultC[i]) > 1e-5) {std::cout << "Result verification failed at index " << i << std::endl;return 1;}}std::cout << "Result verification passed" << std::endl;// 释放设备内存CHECK(cudaFree(deviceA));CHECK(cudaFree(deviceB));CHECK(cudaFree(deviceC));return 0;
}
- Consider the following CUDA kernel and the corresponding host function that
calls it:a. What is the number of threads per block?
b. What is the number of threads in the grid?c. What is the number of blocks in the grid?
d. What is the number of threads that execute the code on line 05?

答案:a、16*32=512;b、48640;c、95;d、45000
- Consider a 2D matrix with a width of 400 and a height of 500. The matrix is
stored as a one-dimensional array. Specify the array index of the matrix
element at row 20 and column 10:
a. If the matrix is stored in row-major order.
b. If the matrix is stored in column-major order.
答案:a、20*400+10=8010
b、10*500+20=5020
Consider a 3D tensor with a width of 400, a height of 500, and a depth of 300
The tensor is stored as a one-dimensional array in row-major order.
Specify the array index of the tensor element at x 5 10, y 5 20, and z 5 5.
答案: 5 * (400 * 500) + 10 * 400 + 5 = 1004005
勘误
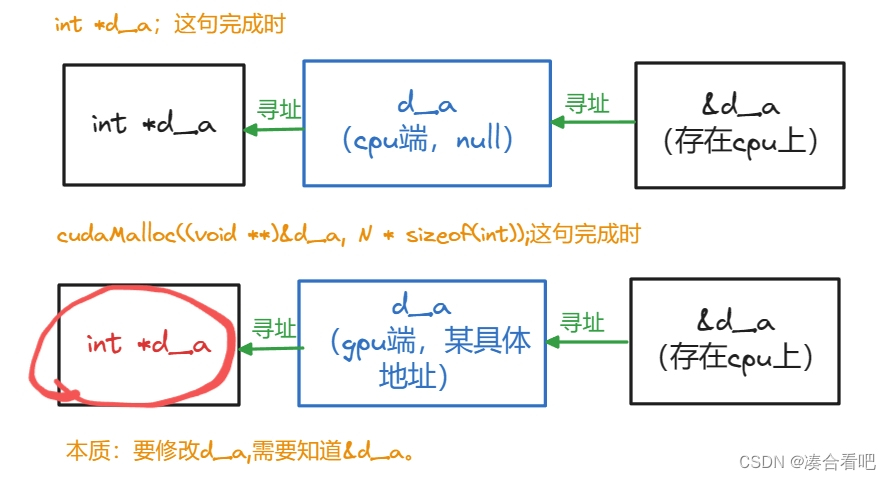
上一篇博客中,这个图里面的d_a的类型写错了,应该是int* d_a,而不是void* d_a。传入函数的是(void**)&d_a,函数结束后,d_a还是int*类型。
