创业做网站需要哪些必备条件今日时政新闻
目录
什么是LinkedList
链表的概念及结构
链表的结构
无头单向非循环链表
addFirst方法(头插法)
addLast方法(尾插法)
addIndex方法
contains方法
removeAllKey方法
size和clear方法
链表oj题
无头双向非循环链表
addFirst方法(头插法)
addLast方法(尾插法)
addIndex方法
contains方法
removeAllKey方法
clear方法
什么是LinkedList
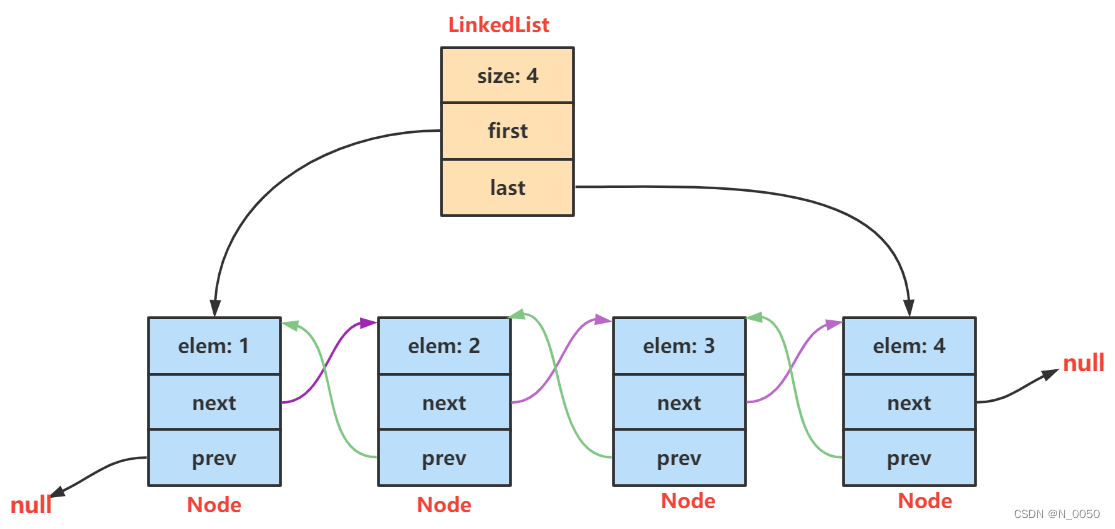
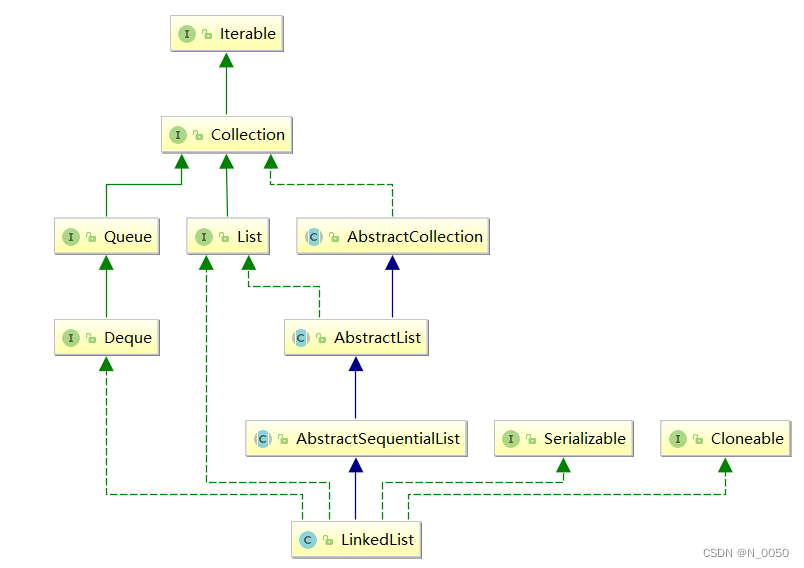
链表的概念及结构
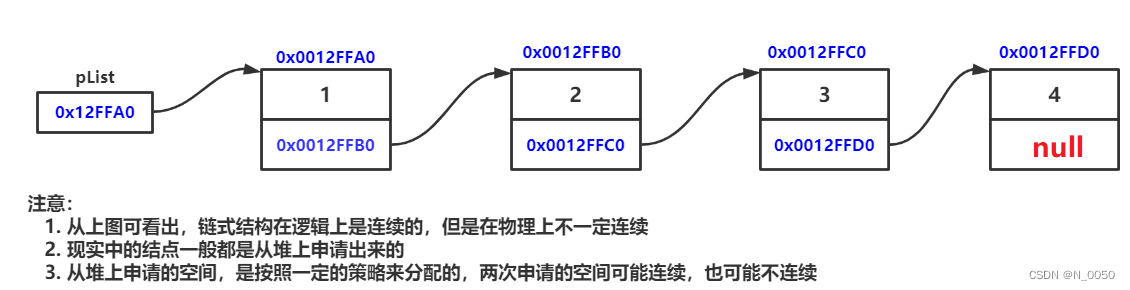
链表的结构
无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。另外这种结构在笔试面试中出现很多
无头双向非循环链表:在Java的集合框架库中LinkedList底层实现就是无头双向循环链表
图中是单向不带头非循环,一整个框代表一个节点就是node
带头的单向非循环,头(head)相当于司机,不能在前面插入

带头的单向循环
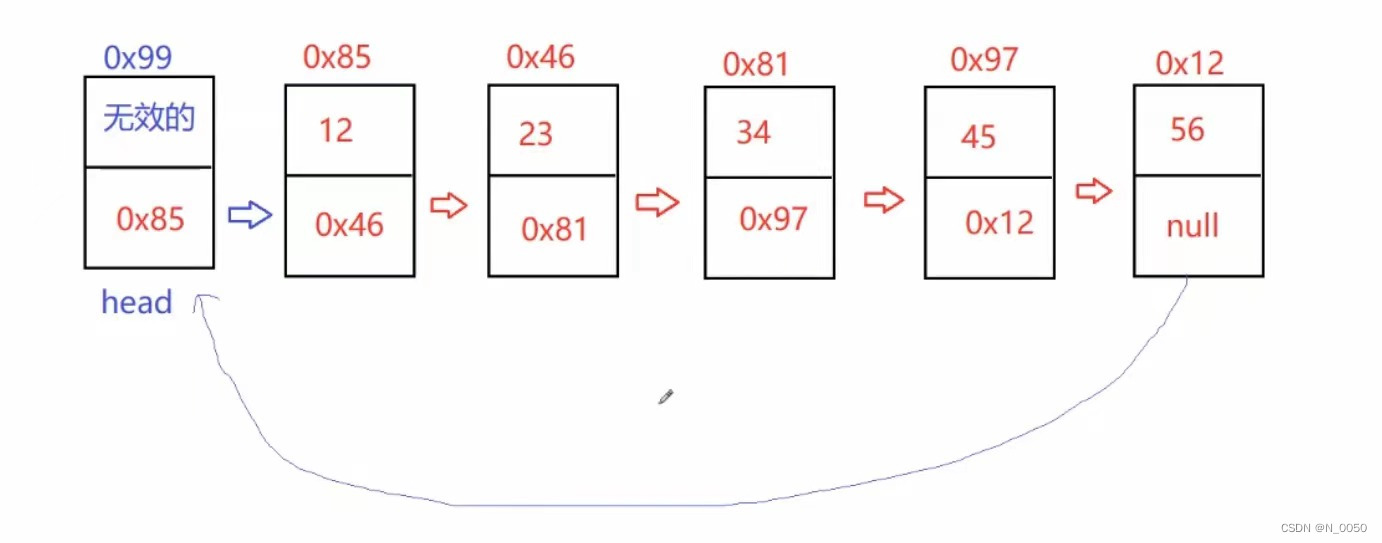
总结:
单向:一直往后走,直到走到head==null
双向:可往后走可往回走,多一个域,后一个存前一个的地址,前一个存的null
带头:前面不可插,head不会变
不带头:前面可插,head会变
循环:循环完回到头(head)
无头单向非循环链表
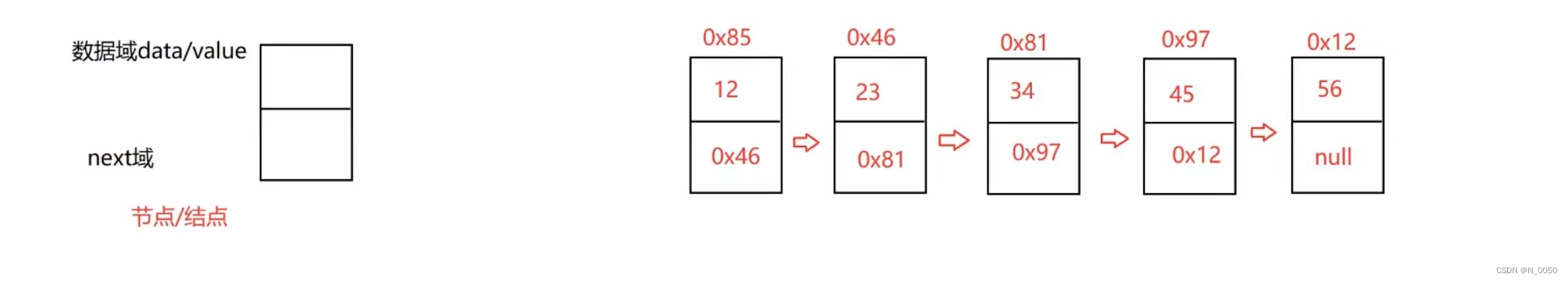
链表的节点由两个域组成,一个是val域,一个是next域,图中的是无头单向非循环链表,下面的
方法都是模拟底层的代码

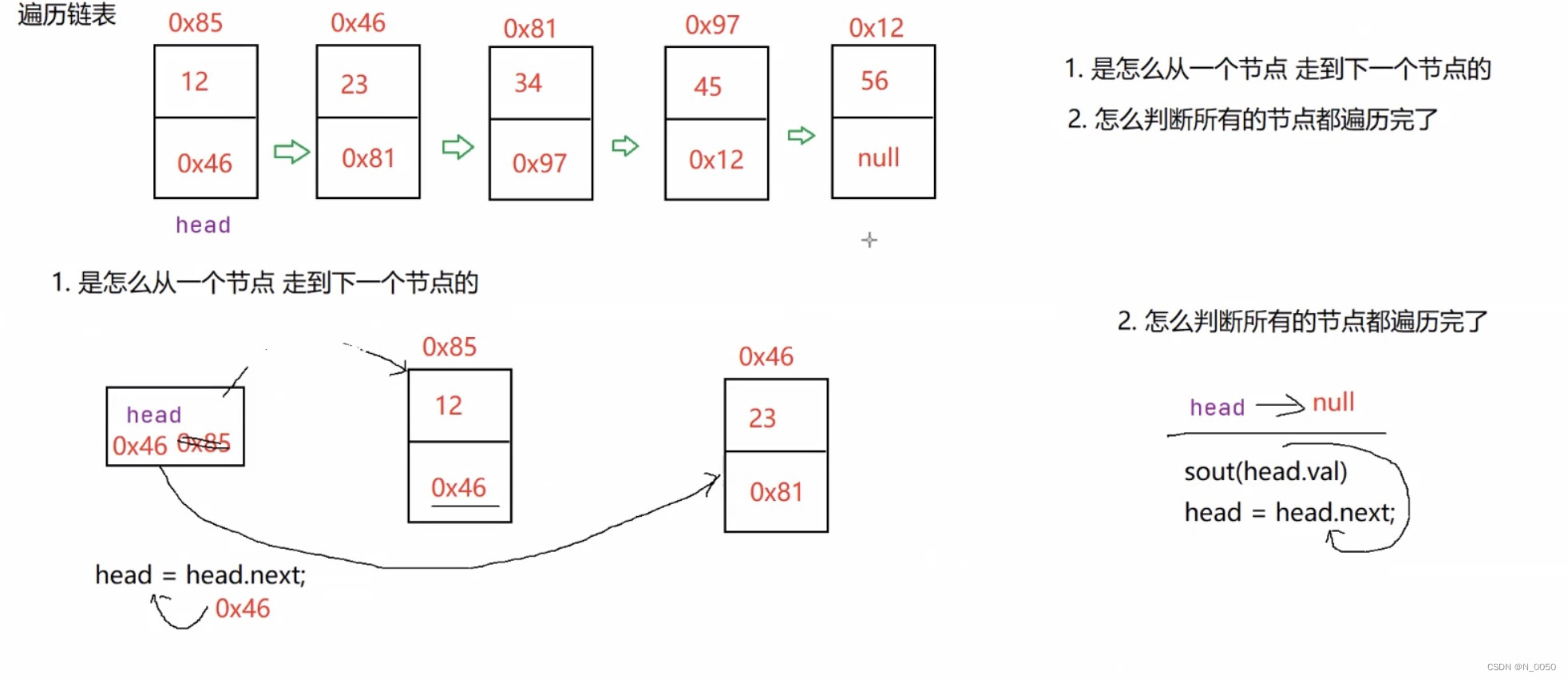
遍历链表:
如何遍历链表呢?
首先每个节点的next域指向的都是下个节点的地址,我们先从第一个节点到第二个节点,
head=head.next,这时候head就来到图中的0x46这个节点了,以此类推,如何判断走完呢,
就是head==null,最后head指向空,以此为结束条件
遍历链表代码:
public void display() {ListNode cur = this.head;//把这个赋给cur,不然方法结束后会没有指向while (cur != null) {//因为最后一个next域里是nullSystem.out.print(cur.val + " ");//打印val域里的值cur = cur.next;//当前节点指向下一个节点的next,,}System.out.println();}addFirst方法(头插法)
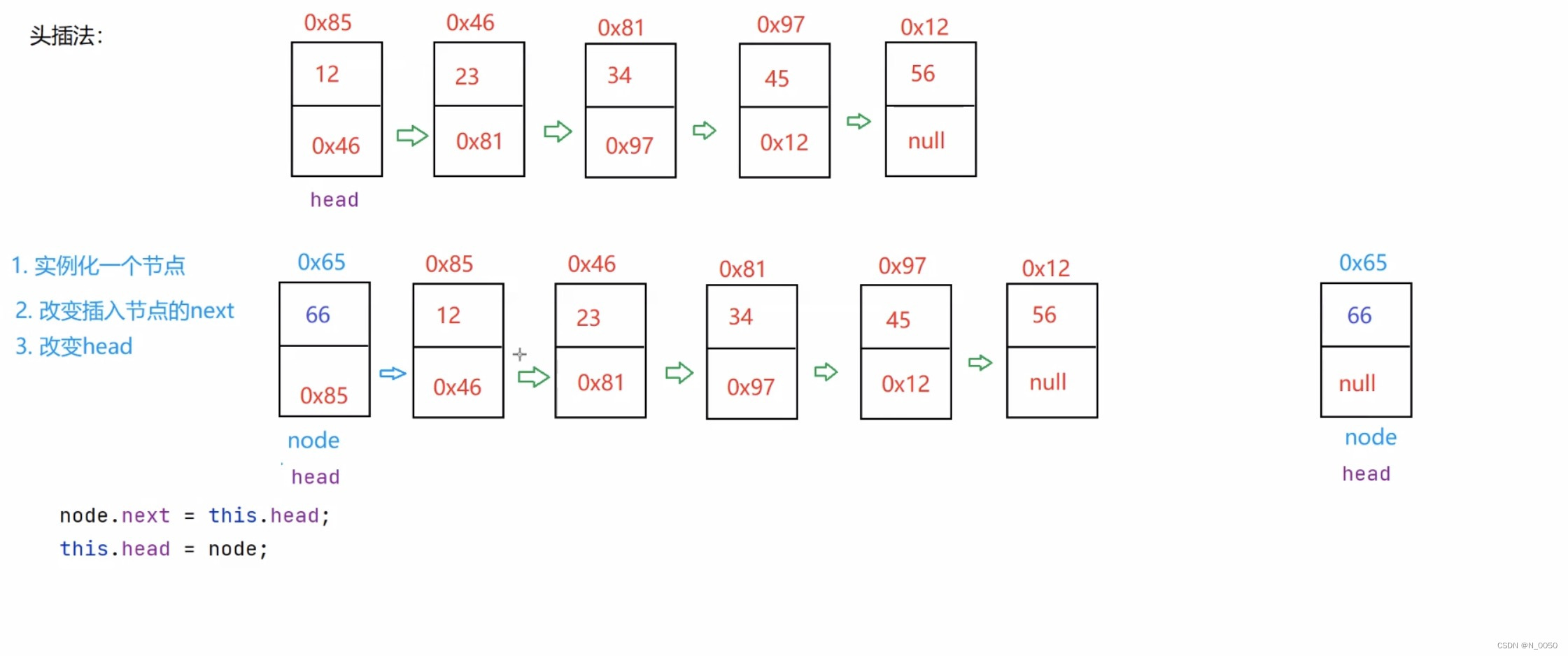
我们使用头插法在head的前面插入一个节点,这个叫头插法,就是把head给到你插入的节点
所以我们要创建一个节点,如下图所示,0x65就是我们创建的节点,一开始创建这个节点的时候
只有val值,它的next域是空的,要想把它放到第一个,我们得把它的next域存的是现在的head的
地址,然后我们在把head指向我们创建的节点,这就是我们的头插法。
头插法代码:
public void addFirst(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);if(this.head == null) {this.head = node;}else {node.next = this.head;this.head = node;}}addLast方法(尾插法)
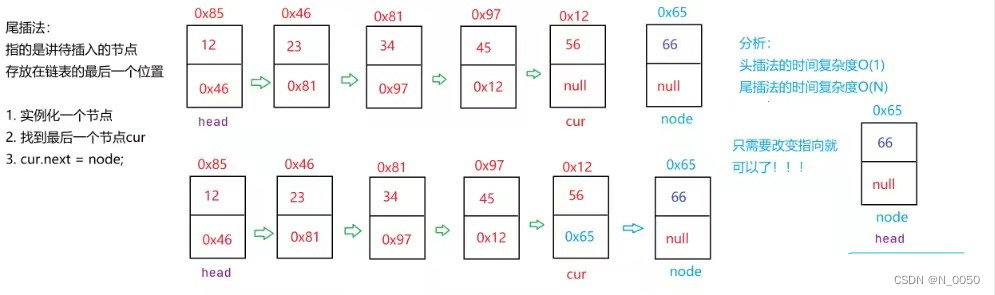
如果我们想要在最后一个节点后面插入一个节点,我们就要使用尾插法,尾插法很简单,我们
设置循环的条件,当我们遍历到head.next==null说明我们来到了最后一个节点,这时候把head的
next域存入你要插入节点的地址就行了。
尾插法代码:
public void addLast(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);ListNode cur = this.head;if(this.head == null) {this.head = node;}else {//找到尾巴while(cur.next != null) {cur = cur.next;}//cur 现在指向了最后一个节点cur.next = node;}}
addIndex方法
这个方法可以根据我们输入的下标以及输入的数字,插入到指定的下标,这时候我们要注意
如果你要插入下标为1的节点,它的前一个节点存的才是你下标为1的节点,你不能直接插下标为1
的节点,你得插入它的前一个节点,这样你才能变成下标为1的节点,所以我们需要创建一个节点
先让它的next域存的是你前一个节点的next域里的地址,然后让你前面节点的next域换成你插入
节点的地址。

具体代码:
代码中还考虑了会不会下标的问题以及当下标等于0和等于链表长度的情况
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {if(index < 0 || index > size()) {//抛自定义的异常return;}if(index == 0) {addFirst(data);return;}if(index == size()) {addLast(data);return;}ListNode cur = searchPrev(index);ListNode node = new ListNode(data);node.next = cur.next;cur.next = node;}private ListNode searchPrev(int index) {ListNode cur = this.head;int count = 0;while (count != index-1 ) {cur = cur.next;count++;}return cur;}contains方法
这个方法很简单就是遍历你的链表,然后判断你的节点val值是不是等于实参传入的值具体实现看
如下代码。
public boolean contains(int key) {ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur != null) {if(cur.val == key) {return true;}cur = cur.next;}return false;}remove方法
删除节点,我们只需要把你要删除数字的节点的前一个节点的next域存的是你要删除的那个数字的
节点的next域里的地址,如图所示,比如你要删除23这个数字,你把12节点的next域的地址改成
23节点next域里的地址就好了。

具体代码:
public void remove(int key) {if(this.head == null) {//一个节点都没有 无法删除!return;}if(this.head.val == key) {this.head = this.head.next;return;}//1. 找到前驱ListNode cur = findPrev(key);//2、判断返回值是否为空?if(cur == null) {System.out.println("没有你要删除的数字");return;}//3、删除ListNode del = cur.next;cur.next = del.next;}/*** 找到关键字key的前一个节点的地址* @param key* @return*/private ListNode findPrev(int key) {ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur.next != null) {if(cur.next.val == key) {return cur;}cur = cur.next;}return null;}removeAllKey方法
我们创建一个prev节点来记录head,再创建一个cur节点记录head的下一个节点,然后如果循环
如果找到了要删除的值,让prev的next域存cur的next域里的地址,如果没找到,prev指向cur,
cur接着指向往下一个节点走。最后再判断是不是头节点是不是要删除的节点,看图配合代码思考
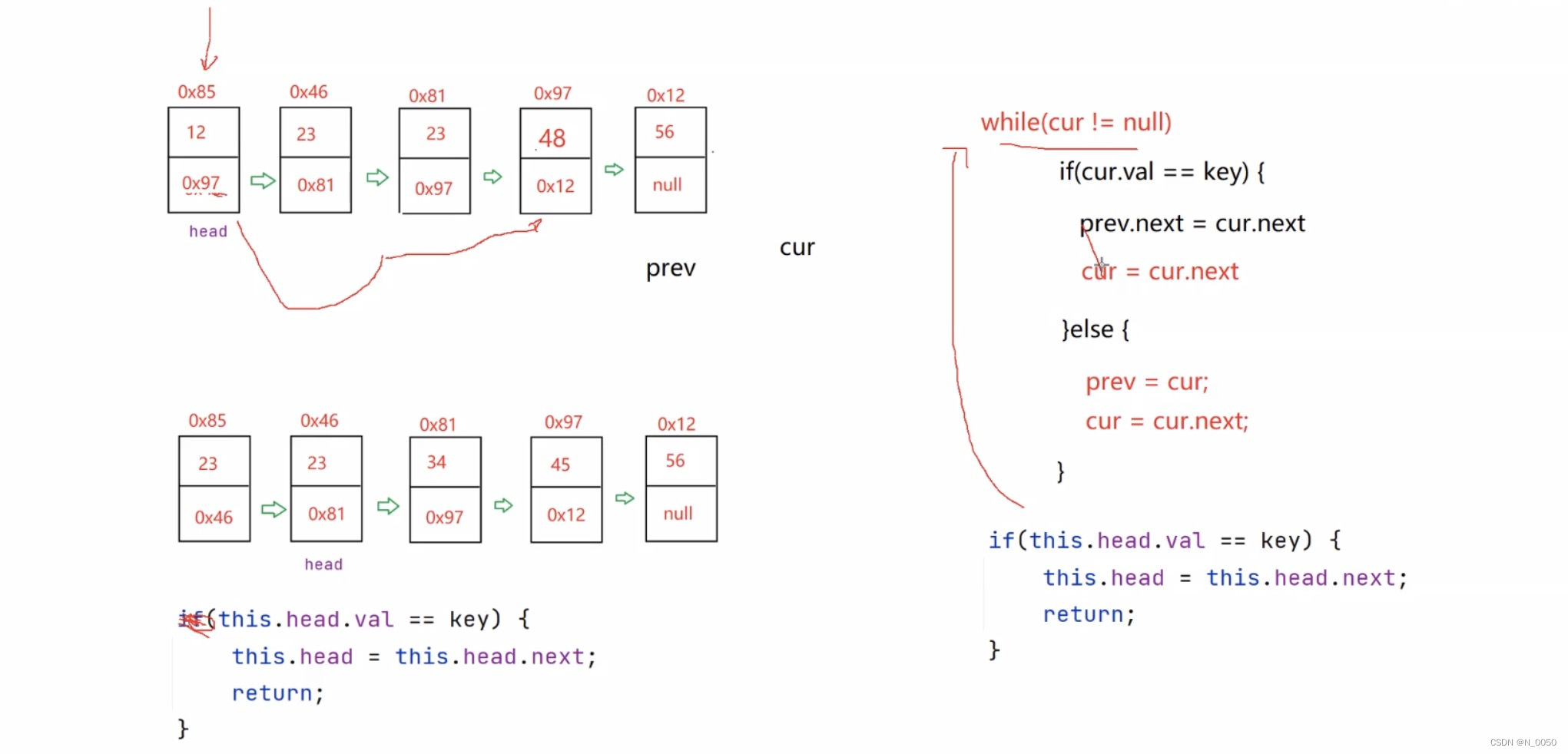
具体代码:
public void removeAllKey(int key) {if (this.head == null) {//一个节点都没有 无法删除!return;}ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.next.val == key) {cur.next = cur.next.next;}cur = cur.next;}//如果头的val域的值就是key,把当前head指向下一个if (head.val == key) {head = head.next;}}size和clear方法
size方法我们只需要设置一个变量来记录循环的次数,就是在遍历链表的基础上加个变量,clear
方法就设置一个节点存你要删除的当前的next域的地址,然后再把当前节点的next域设置为空,然
后循环到指向空停止,具体实现看代码。
public int size() {int count = 0;ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur != null) {count++;cur = cur.next;}return count;}public void clear() {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {ListNode curNext = cur.next;//cur.val = null;cur.next = null;cur = curNext;}head = null;}链表oj题
下面的代码我都是在idea上写的,在leetcode里记得修改
1. 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/
代码:
public void removeAllKey(int key) {if(this.head == null) {return;}ListNode prev = head;ListNode cur = head.next;while (cur != null) {if(cur.val == key) {prev.next = cur.next;cur = cur.next;}else {prev = cur;cur = cur.next;}}if (head.val == key) {head = head.next;}}2. 反转一个单链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/
代码:
public ListNode reverseList() {if(head == null) {return null;}//只有一个节点if(head.next == null) {return head;}ListNode cur = head.next;head.next = null;while (cur != null) {ListNode curNext = cur.next;cur.next = head;head = cur;cur = curNext;}return head;}3. 给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/description/
代码:
public ListNode middleNode2() {ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;while (fast != null && fast.next != null){fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;}return slow;}4. 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/529d3ae5a407492994ad2a246518148a?tpId=13&&tqId=11167&rp=2&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking
代码:
public ListNode findKthToTail(int k) {if(k <= 0 || head == null ) {return null;}ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;int count = 0;while (k-1 != count) {fast = fast.next;//处理 K 太大的问题if(fast == null) {return null;}count++;}while (fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next;slow = slow.next;}return slow;}5. 将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的
https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/description/
代码:
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {ListNode newH = new ListNode(0);ListNode tempH = newH;while (head1 != null && head2 != null) {if (head1.val < head2.val) {tempH.next = head1;head1 = head1.next;} else {tempH.next = head2;head2 = head2.next;}tempH = tempH.next;}if (head1 != null) {tempH.next = head1;}if (head2 != null) {tempH.next = head2;}return newH.next;}7. 链表的回文结构
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d281619e4b3e4a60a2cc66ea32855bfa?tpId=49&&tqId=29370&rp=1&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/2016test/question-ranking
代码:
public boolean chkPalindrome() {if(head == null || head.next == null) {return true;}// write code hereListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;//1、找到中间位置while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;}//2、翻转ListNode cur = slow.next;while (cur != null) {ListNode curNext = cur.next;cur.next = slow;slow = cur;cur = curNext;}//3、从前到后 从后到前while (head != slow) {if(head.val != slow.val) {return false;}if(head.next == slow) {return true;}head = head.next;slow = slow.next;}return true;}6. 编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/0e27e0b064de4eacac178676ef9c9d70?tpId=8&&tqId=11004&rp=2&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/cracking-the-coding-interview/question-ranking
代码:
public ListNode partition(ListNode pHead, int x) {// write code hereif(pHead == null) {return null;}ListNode bs = null;ListNode be = null;ListNode as = null;ListNode ae = null;ListNode cur = pHead;while(cur != null) {if(cur.val < x) {if(bs == null) {//插入第一个节点bs = cur;be = cur;}else {be.next = cur;be = be.next;}}else {if(as == null) {as = cur;ae = cur;}else {ae.next= cur;ae = ae.next;}}cur = cur.next;}//开始串起来if(bs == null) {//第一个区间没有数据return as;}//第一个区间有数据be.next = as;if(as != null) {//第2个区间有数据ae.next = null;}return bs;}8. 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/description/
代码:
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {ListNode pl = headA;ListNode ps = headB;//1、求长度int lengthA = 0;while (pl != null) {lengthA++;pl = pl.next;}int lengthB = 0;while (ps != null) {lengthB++;ps = ps.next;}pl = headA;ps = headB;int len = lengthA - lengthB;if (len < 0) {//如果长度为负,说明后面那个长度大//修正一下 pl和ps的指向pl = headB;ps = headA;len = lengthB - lengthA;//把长度弄正的}//代码执行到这里// 1. pl一定指向最长的链表,ps一定指向最短的链表 2. len一定是一个正数//2、走差值步while (len != 0) {//最长的走差值步pl = pl.next;len--;}//3、同时走 //4、相遇就是相遇点while (pl != ps) {pl = pl.next;ps = ps.next;if (pl == null) {return null;}}return pl;}9. 给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环
https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/description/
代码:
public boolean hasCycle2(ListNode head) {ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;if(fast == slow) {break;}}if(fast == null || fast.next == null) {return false;}return true;}10. 给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 NULL
https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/
代码:
public ListNode hasCycle3(ListNode head) {ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;if (fast == slow) {break;}}if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {return null;}slow = head;//slow从head出发,fast从相遇点出发,一人一步,走到最后就是入口点while (slow != fast) {fast = fast.next;slow = slow.next;}return slow;}无头双向非循环链表
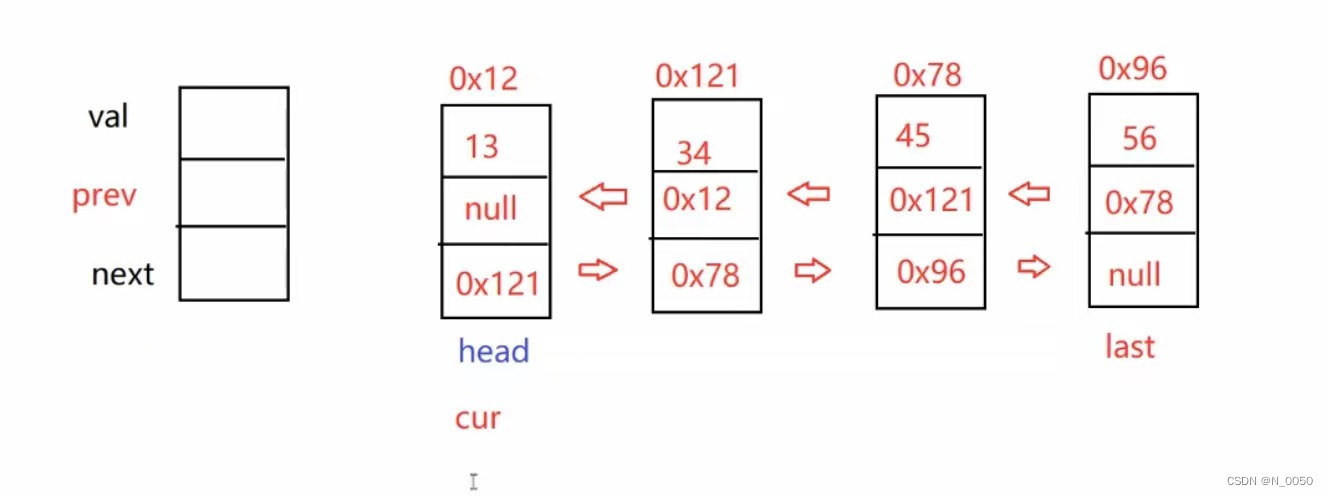
addFirst方法(头插法)
首先,我们先创建一个节点,然后我们把当前head的prev域存入你插入节点的地址,因为我们现
在的head的prev域里是空,为了保证他是双向循环,所以prev得设置一下,然后在把你新创建节
点的next域存入head的地址,最后再把head指向你插入的节点。看下图联想一下

具体代码:
public void addFirst(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);if(head == null) {head = node;last = node;}else {node.next = head;head.prev = node;head = node;}}addLast方法(尾插法)
尾插法同样我们需要创建一个对象,我们只需要把last的next域存你插入节点的地址,然后把你插
入节点的prev域存你当前last的地址,最后再把last指向你插入的节点,想不通看下图。
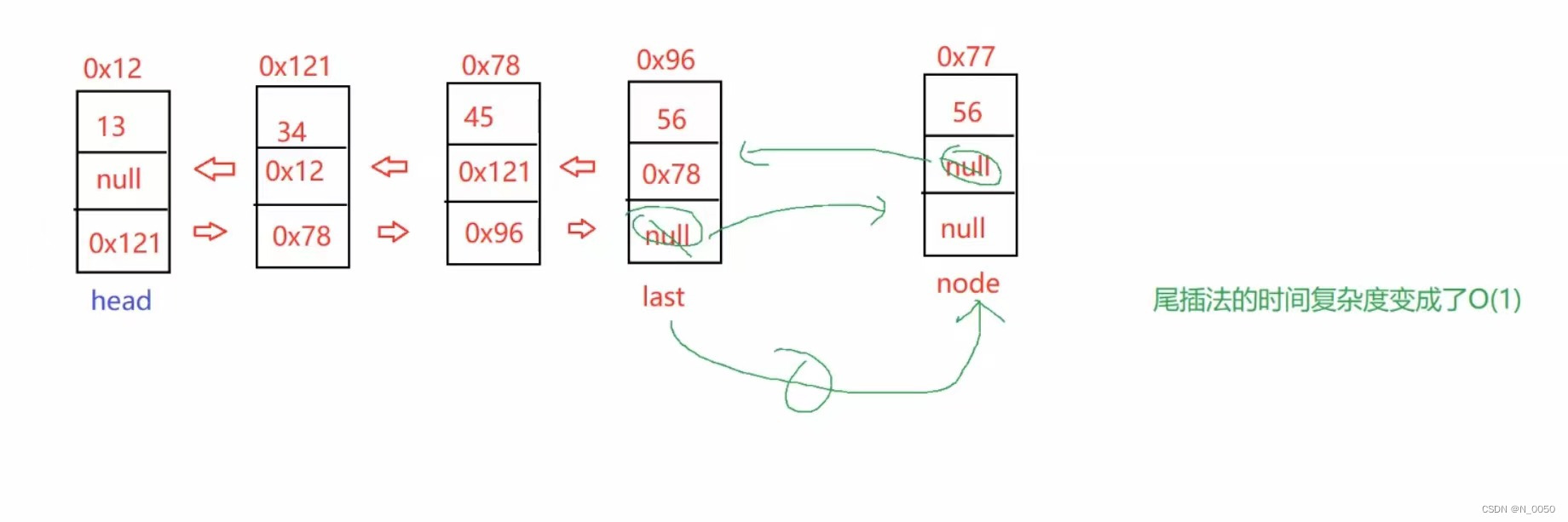
具体代码:
public void addLast(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);if(head == null) {head = node;last = node;}else {last.next = node;node.prev = last;last = node;}}addIndex方法
如图所示,我们可以让head先走,走到你要插入的下标,对比单向的它不需要停在你要插入下标
的前一个节点,因为在双向我们知道前一个节点的地址,先假设我们要插入下标为2的节点,然后
我们创建一个节点,,然后把它的next域存你要下标为2节点的地址,随后我们把下标为2的前一
个节点的地址改成你插入节点的地址,然后prev域存下标为2的prev域的地址,然后再把下标为2
的prev改成你插入节点的地址就好了。
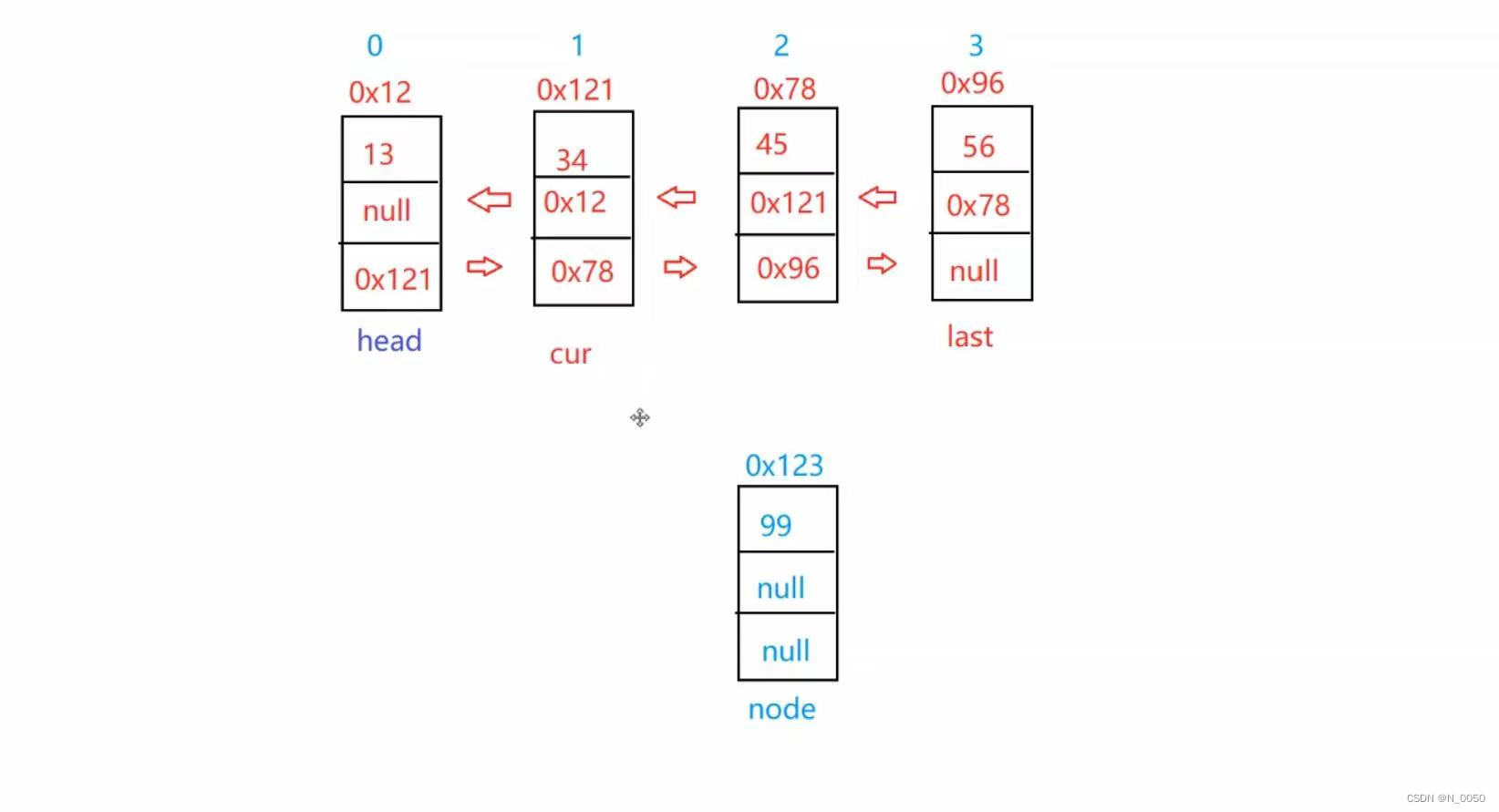
具体代码:
public void addIndex(int index, int data) throws PosException {int len = size();//这样写size方法只用调用一次if (index < 0 || index > len) {throw new PosException("插入下标异常!");}if (index == 0) {addFirst(data);return;}if (index == len) {addLast(data);return;}ListNode cur = head;ListNode node = new ListNode(data);int count = 0;while (count != index) {count++;cur = cur.next;}node.next = cur;cur.prev.next = node;node.prev = cur.prev;cur.prev = node;}contains方法
跟单向的一样的代码一样
public boolean contains(int key) {if (head == null) {return false;}ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == key) {return true;}cur = cur.next;}return false;}remove方法
双向的这个方法很复杂,需要考虑到很多方面,一步一步来,先最简单的就head停留在你要删除
的节点,然后把它的前一个节点的next域指向你要删除节点的next域的地址,然后还要把后一个数
字的prev域改成你要删除的数字前一个节点的地址。这是最简单的情况,然后就是如果是一开始
head节点的就是你要删除的节点的情况,我们先让head往下一个节点这样就删掉了,然后判断
这时候的head是不是指向空,如果是last也得为空,因为只有一个节点。然后如果是last节点是你
要删除都节点的情况,我们得让last的前一个节点的next域指向空,然后last指向前一个节点。然
后就是中间的情况,先让你要删除节点的前一个节点的next指向删除节点next域里的地址,然后让
它后一个节点的prev域存要删除节点的前一个节点的地址。想不通结合下图想想
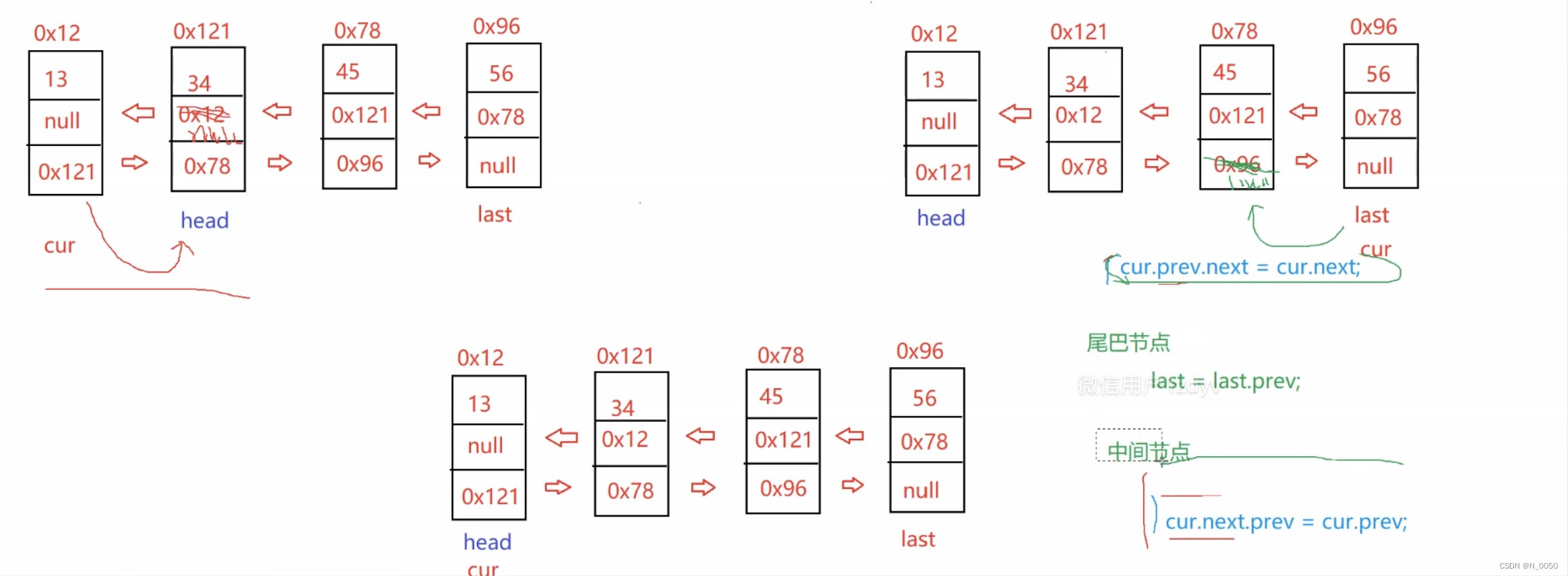
具体代码:
public void remove(int key) {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == key) {if (cur == head) {//如果head的val等于keyhead = head.next;//head == nullif (head == null) {last = null;} else {//head到下个节点且不为空head.prev = null;}} else {cur.prev.next = cur.next;//中间等于keyif (cur == last) {//如果last的val等于keylast = last.prev;} else {cur.next.prev = cur.prev;}}return;} else {cur = cur.next;}}}removeAllKey方法
跟remove几乎一样就是找到了要删除的节点还得继续往下走直到删除完所有要删除的
具体代码:
public void removeAllKey(int key) {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == key) {if (cur == head) {//如果head的val等于keyhead = head.next;//head == nullif (head == null) {last = null;} else {//head到下个节点且不为空head.prev = null;}} else {cur.prev.next = cur.next;//中间等于keyif (cur == last) {//如果last的val等于keylast = last.prev;} else {cur.next.prev = cur.prev;}}}cur = cur.next;}}clear方法
跟单向的一样,多了一个就是让last也指向空
具体代码:
public void clear() {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {ListNode curNext = cur.next;//cur.val = null;cur.prev = null;cur.next = null;cur = curNext;}head = null;last = null;}