珠海集团网站建设报价seo常用方法
本文有部分借鉴 wowo tech ,感谢作者的无私分享
目录
1、简介
2、Platform 软件架构
3、Platform 模块向其它模块提供的 APIs
3.1、数据结构
3.1.1、platform_device
3.1.2、platform_driver
3.2、APIs
3.2.1、Platform Device 提供的 APIs
3.2.2、Platform Driver 提供的 APIs
4、Platform 初始化
4.1、Platform 总线初始化
5、Device 和 Driver 匹配执行 probe
5.1、platform_driver_register 情况
5.2、platform_device_register 情况
5.3、小结
1、简介
在Linux设备模型的抽象中,存在着一类称作“Platform Device”的设备,内核是这样描述它们的(Documentation/driver-model/platform.txt):
Platform devices are devices that typically appear as autonomous entities in the system. This includes legacy port-based devices and host bridges to peripheral buses, and most controllers integrated into system-on-chip platforms. What they usually have in common is direct addressing from a CPU bus. Rarely, a platform_device will be connected through a segment of some other kind of bus; but its registers will still be directly addressable.
概括来说,Platform设备包括:基于端口的设备(已不推荐使用,保留下来只为兼容旧设备,legacy);连接物理总线的桥设备;集成在SOC平台上面的控制器;连接在其它bus上的设备(很少见)。等等。
这些设备有一个基本的特征:可以通过CPU bus直接寻址(例如在嵌入式系统常见的“寄存器”)。因此,由于这个共性,内核在设备模型的基础上(device和device_driver),对这些设备进行了更进一步的封装,抽象出paltform bus、platform device和platform driver,以便驱动开发人员可以方便的开发这类设备的驱动。
platform总线是虚拟的平台总线,是linux设备驱动模型为了保持设备驱动的统一性而虚拟出来的总线。
总线将设备和驱动绑定,系统每注册一个设备的时候,会寻找与之匹配的驱动;相反,系统每注册一个驱动的时候,会寻找与之匹配的设备,而匹配由总线完成。
可以说,paltform设备对Linux驱动工程师是非常重要的,因为我们编写的大多数设备驱动,都是为了驱动plaftom设备。本文我们就来看看Platform设备在内核中的实现。
2、Platform 软件架构
内核中Platform设备有关的实现位于 include/linux/platform_device.h 和 drivers/base/platform.c 两个文件中,它的软件架构如下:
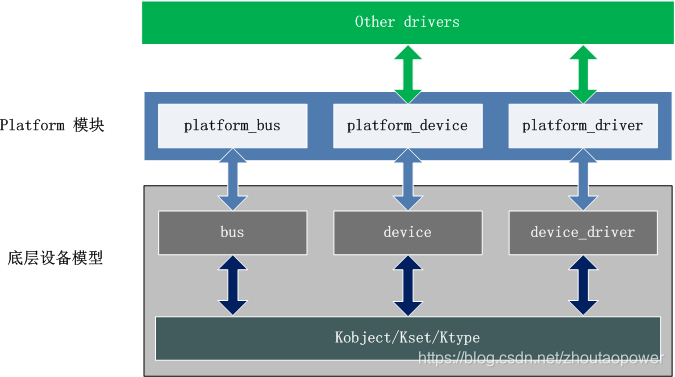
由图片可知,Platform设备在内核中的实现主要包括三个部分:
Platform Bus:基于底层bus模块,抽象出一个虚拟的Platform bus,用于挂载Platform设备;
Platform Device:基于底层device模块,抽象出Platform Device,用于表示Platform设备;
Platform Driver:基于底层device_driver模块,抽象出Platform Driver,用于驱动Platform设备。
3、Platform 模块向其它模块提供的 APIs
Platform 提供的接口包括:Platform Device 和 Platform Driver 两个数据结构,以及它们的操作函数。
3.1、数据结构
3.1.1、platform_device
platform_device 代表了一种 device,定义在 include/linux/platform_device.h 文件
struct platform_device {const char * name;int id;struct device dev;u32 num_resources;struct resource * resource;const struct platform_device_id *id_entry;/* MFD cell pointer */struct mfd_cell *mfd_cell;/* arch specific additions */struct pdev_archdata archdata;
};它的字段解释如下:
dev:真正的设备(Platform设备只是一个特殊的设备,因此其核心逻辑还是由底层的模块实现)。
name:设备的名称,和 struct device 结构中的 init_name 一样。实际上,该名称在设备注册时,会拷贝到 dev.init_name中。
id:用于表示该设备的 ID。
id_auto:指示在注册设备时,是否自动赋予ID值(不需要人为指定啦,可以懒一点啦)。
num_resources、resource:该设备的资源描述,由struct resource(include/linux/ioport.h)结构抽象。
在Linux中,系统资源包括I/O、Memory、Register、IRQ、DMA、Bus等多种类型。这些资源大多具有独占性,不允许多个设备同时使用,因此Linux内核提供了一些API,用于分配、管理这些资源。
当某个设备需要使用某些资源时,只需利用struct resource组织这些资源(如名称、类型、起始、结束地址等),并保存在该设备的resource指针中即可。然后在设备probe时,设备需求会调用资源管理接口,分配、使用这些资源。而内核的资源管理逻辑,可以判断这些资源是否已被使用、是否可被使用等等。id_entry:和内核模块相关的内容,暂不说明。
mfd_cell:和MFD设备相关的内容,暂不说明。
archdata:不管它了
可以看出 platform_device 其实是裹了一层 struct device 的一种设备的抽象。
3.1.2、platform_driver
platform_driver 是一种特殊的 driver,它定义在 include/linux/platform_device.h 文件:
struct platform_driver {int (*probe)(struct platform_device *);int (*remove)(struct platform_device *);void (*shutdown)(struct platform_device *);int (*suspend)(struct platform_device *, pm_message_t state);int (*resume)(struct platform_device *);struct device_driver driver;const struct platform_device_id *id_table;
};struct platform_driver结构和struct device_driver非常类似,无非就是提供probe、remove、suspend、resume等回调函数,这里不再细说。
另外这里有一个 id_table 的指针,该指针和 of_match_table、acpi_match_table 的功能类似:提供其它方式的设备probe。 内核会在合适的时机检查device和device_driver的名字,如果匹配,则执行probe。其实除了名称之外,还有一些宽泛的匹配方式,例如这里提到的各种match table,具体原理就先不罗嗦了,徒添烦恼!就当没看见,呵呵。
3.2、APIs
3.2.1、Platform Device 提供的 APIs
Platform Device主要提供设备的分配、注册等接口,供其它driver使用,常用的包括:
1、注册/注销一个 Platform 设备:
int platform_device_register(struct platform_device *);
void platform_device_unregister(struct platform_device *);int platform_add_devices(struct platform_device **, int); // 增加多个 devices
2、获取资源:
struct resource *platform_get_resource(struct platform_device *,unsigned int, unsigned int);struct resource *platform_get_resource_byname(struct platform_device *,unsigned int,const char *);3、获取 irq:
int platform_get_irq(struct platform_device *, unsigned int);
int platform_get_irq_byname(struct platform_device *, const char *);4、向 platform_device 增加资源:
int platform_device_add_resources(struct platform_device *pdev,const struct resource *res,unsigned int num);
5、向 platform device 中添加自定义的数据(保存在pdev->dev.platform_data指针中)
int platform_device_add_data(struct platform_device *pdev,const void *data, size_t size);
3.2.2、Platform Driver 提供的 APIs
Platform Driver提供struct platform_driver的分配、注册等功能,常用的包括:
1、注册/注销 platform_driver 接口:
int platform_driver_register(struct platform_driver *);
void platform_driver_unregister(struct platform_driver *);2、主动执行 probe 动作接口:
int platform_driver_probe(struct platform_driver *driver,int (*probe)(struct platform_device *));3、设置/获取私有数据接口:
inline void *platform_get_drvdata(const struct platform_device *pdev);
inline void platform_set_drvdata(struct platform_device *pdev,void *data)
4、Platform 初始化
platform驱动工作流程:
1. 系统开机内核初始化阶段,初始化 platform 总线;
2. platform_device 初始化调用 platform_add_devices(一次注册多个设备)或者 platform_device_register(一次注册单个设备),这部分一般在 arch/arm/mach 配置文件中,在上电开机的时候完成 platform_device 初始化 ;
3. platform_driver 的初始化调用 platform_driver_register 或者 driver_register,该过程一般在驱动程序的 init 函数中;
4.1、Platform 总线初始化
内核在启动过程中,会调用到 kernel_init() –> do_basic_setup() –> driver_init() –> platform_bus_init() 相关的东西就在这里初始化的 driver/base/platform.c:
int __init platform_bus_init(void)
{int error;early_platform_cleanup();error = device_register(&platform_bus); ------- (1)if (error)return error;error = bus_register(&platform_bus_type); --- (2)if (error)device_unregister(&platform_bus);return error;
}先看(1)部分,通过 device_register 它注册了一个 platform_bus 的设备,它的定义在 driver/base ,是:
struct device platform_bus = {.init_name = "platform",
};
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(platform_bus);定义一个名为 platform 的总线设备,其他的platform设备都是它的子设备,所以这里先注册这个设备!
在看(2)部分,通过 bus_register 注册了一个 platform_bus_type 的 bus,它定义是:
struct bus_type platform_bus_type = {.name = "platform",.dev_attrs = platform_dev_attrs,.match = platform_match,.uevent = platform_uevent,.pm = &platform_dev_pm_ops,
};
注册平台类型的 bus,将出现 sys 文件系统在 bus 目录下,创建一个 platform 的目录,以及相关属性文件。
这里创建好 platform 的 bus 了,就等相关的设备驱动去注册自己的 platform_device 和 platform_driver;
这里我们着重关心一下 probe 的执行时机。
5、Device 和 Driver 匹配执行 probe
现在 platform_bus 已经 Ready,那么我们的 device 和 driver 是如何 match 上,并且执行 driver 的 probe 的呢?
在总线上 device 和 driver 的名字匹配,就会调用 driver 的 probe 函数;
那么就会存在一个问题,到底是先有 device 还是先有 driver,因为他们俩注册肯定是有先后顺序的,所以需要看看源代码
5.1、platform_driver_register 情况
platform_driver_register 实现了注册一个 platform_driver,它的代码在 driver/base/platform.c :
/*** platform_driver_register - register a driver for platform-level devices* @drv: platform driver structure*/
int platform_driver_register(struct platform_driver *drv)
{drv->driver.bus = &platform_bus_type;if (drv->probe)drv->driver.probe = platform_drv_probe;if (drv->remove)drv->driver.remove = platform_drv_remove;if (drv->shutdown)drv->driver.shutdown = platform_drv_shutdown;return driver_register(&drv->driver);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(platform_driver_register);先把 driver 的 bus 赋值成为了 platform_bus_type,代表是属于 platform bus 的,最后直接调用到 driver_register 注册到更底层的设备模型,它的代码在 driver/base/driver.c:
int driver_register(struct device_driver *drv)
{int ret;struct device_driver *other;BUG_ON(!drv->bus->p);if ((drv->bus->probe && drv->probe) ||(drv->bus->remove && drv->remove) ||(drv->bus->shutdown && drv->shutdown))printk(KERN_WARNING "Driver '%s' needs updating - please use ""bus_type methods\n", drv->name);other = driver_find(drv->name, drv->bus); ------------(1)if (other) {put_driver(other);printk(KERN_ERR "Error: Driver '%s' is already registered, ""aborting...\n", drv->name);return -EBUSY;}ret = bus_add_driver(drv); ----------------------------(2)if (ret)return ret;ret = driver_add_groups(drv, drv->groups);if (ret)bus_remove_driver(drv);return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(driver_register);先看(1),调用了 driver_find:
struct device_driver *driver_find(const char *name, struct bus_type *bus)
{struct kobject *k = kset_find_obj(bus->p->drivers_kset, name);struct driver_private *priv;if (k) {priv = to_driver(k);return priv->driver;}return NULL;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(driver_find);
看看核心函数 kset_find_obj:
struct kobject *kset_find_obj(struct kset *kset, const char *name)
{return kset_find_obj_hinted(kset, name, NULL);
}struct kobject *kset_find_obj_hinted(struct kset *kset, const char *name,struct kobject *hint)
{struct kobject *k;struct kobject *ret = NULL;
.........list_for_each_entry(k, &kset->list, entry) {if (kobject_name(k) && !strcmp(kobject_name(k), name)) {ret = kobject_get(k);break;}}
.........
}
kset_find_obj通过循环操作,根据我们给的名字name在指定的bus中循环对比,查看是否有相同的名字name(这个name存放在kobj中)。其实这就是一个循环链表的遍历过程
所以,driver_find 通过我们给定的name在某bus中寻找驱动,比对名字,看看驱动是否已经装载!
总结driver_find过程如下:
1. driver_find,拿到了drv->name和drv->bus开始找驱动
2. kset_find_obj 通过driver_find传递的bus->p->drivers_kset,利用list_for_each_entry遍历kset循环链表。(kset结构体中有循环链表指针next和prev)
3. 遍历循环链表中每一个kobj中的成员变量name
4. 通过strcmp(kobject_name(k), name)比较drv->name 和kobj中的name,如果有相同则表示查找成功
5. return :如果找到,则返回device_driver的指针,如果没有找到则返回了NULL。
返回到 driver_register 函数,如果已经装载了驱动,那么直接返回 -EBUSY
在看 (2),bus_add_driver:
int bus_add_driver(struct device_driver *drv)
{struct bus_type *bus;struct driver_private *priv;int error = 0;bus = bus_get(drv->bus);if (!bus)return -EINVAL;
....priv = kzalloc(sizeof(*priv), GFP_KERNEL);
....klist_init(&priv->klist_devices, NULL, NULL);
....if (drv->bus->p->drivers_autoprobe) {error = driver_attach(drv);if (error)goto out_unregister;}
....
}内容较多,略去了部分内容,主要是王指定的 bus 上增加 driver,同时给底层的 kobject,kset 等等赋值,添加链表等等,这里我们关心:
if (drv->bus->p->drivers_autoprobe) {error = driver_attach(drv);if (error)goto out_unregister;}这个 drv->bus->p->drivers_autoprobe,其实就是 platform_bus_type->subsys_private->drivers_autoprobe 的值,在初始化 platform_bus 的时候,调用 bus_register 的时候,这个值没有设置,被默认设置成为了 1:
int bus_register(struct bus_type *bus)
{int retval;struct subsys_private *priv;priv = kzalloc(sizeof(struct subsys_private), GFP_KERNEL);if (!priv)return -ENOMEM;priv->subsys.kobj.kset = bus_kset;priv->subsys.kobj.ktype = &bus_ktype;priv->drivers_autoprobe = 1;}所以,这里将会执行到 driver_attach:
int driver_attach(struct device_driver *drv)
{return bus_for_each_dev(drv->bus, NULL, drv, __driver_attach);
}int bus_for_each_dev(struct bus_type *bus, struct device *start,void *data, int (*fn)(struct device *, void *))
{struct klist_iter i;struct device *dev;int error = 0;if (!bus)return -EINVAL;klist_iter_init_node(&bus->p->klist_devices, &i,(start ? &start->p->knode_bus : NULL));while ((dev = next_device(&i)) && !error)error = fn(dev, data);klist_iter_exit(&i);return error;
}进而执行到 __driver_attach 函数:
static int __driver_attach(struct device *dev, void *data)
{struct device_driver *drv = data;/** Lock device and try to bind to it. We drop the error* here and always return 0, because we need to keep trying* to bind to devices and some drivers will return an error* simply if it didn't support the device.** driver_probe_device() will spit a warning if there* is an error.*/if (!driver_match_device(drv, dev))return 0;if (dev->parent) /* Needed for USB */device_lock(dev->parent);device_lock(dev);if (!dev->driver)driver_probe_device(drv, dev);device_unlock(dev);if (dev->parent)device_unlock(dev->parent);return 0;
}看注释,希望在前方,这个 driver_match_device 函数
static inline int driver_match_device(struct device_driver *drv,struct device *dev)
{return drv->bus->match ? drv->bus->match(dev, drv) : 1;
}其实便是执行到了 platform_bus 的 platform_match:
static int platform_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev);struct platform_driver *pdrv = to_platform_driver(drv);/* Attempt an OF style match first */if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))return 1;/* Then try to match against the id table */if (pdrv->id_table)return platform_match_id(pdrv->id_table, pdev) != NULL;/* fall-back to driver name match */return (strcmp(pdev->name, drv->name) == 0);
}可以看到,有多种 match 上的方式,当然,最简单的还是 name 一致!
当 match 上了后,执行 __driver_attach 的 driver_probe_device 函数调用:
int driver_probe_device(struct device_driver *drv, struct device *dev)
{int ret = 0;if (!device_is_registered(dev))return -ENODEV;pr_debug("bus: '%s': %s: matched device %s with driver %s\n",drv->bus->name, __func__, dev_name(dev), drv->name);pm_runtime_get_noresume(dev);pm_runtime_barrier(dev);ret = really_probe(dev, drv);pm_runtime_put_sync(dev);return ret;
}直接走到了 really_probe 函数,看来快看到想要的了:
static int really_probe(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{int ret = 0;
...atomic_inc(&probe_count);
...dev->driver = drv;
...if (dev->bus->probe) {ret = dev->bus->probe(dev);if (ret)goto probe_failed;} else if (drv->probe) {ret = drv->probe(dev);if (ret)goto probe_failed;}
...
}这里执行到了 driver->probe 函数!!
总体的流程是:
platform_driver_register -> driver_register
-> bus_add_driver
-> driver_attach -> __driver_attach
-> match ? (0 return 1 ->)
-> driver_probe_device (matched)
-> really_probe
-> probe
所以执行到 driver 的 probe 的前提是,match 成功,也就是,device 先存在了,再去注册 driver 的情况,我们再来看看另外一种情况!
5.2、platform_device_register 情况
直接看实现:
int platform_device_register(struct platform_device *pdev)
{device_initialize(&pdev->dev);return platform_device_add(pdev);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(platform_device_register);先将 platform_device 的 device 结构初始化,然后调用 platform_device_add:
int platform_device_add(struct platform_device *pdev)
{int i, ret = 0;if (!pdev)return -EINVAL;if (!pdev->dev.parent)pdev->dev.parent = &platform_bus;pdev->dev.bus = &platform_bus_type;
....if (pdev->id != -1)dev_set_name(&pdev->dev, "%s.%d", pdev->name, pdev->id);elsedev_set_name(&pdev->dev, "%s", pdev->name);
....ret = device_add(&pdev->dev);if (ret == 0)return ret;}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(platform_device_add);设置 bus 为 platform bus type 后,算是挂靠到这个 bus 上,然后做一些初始化的动作,调用到 device_add,进入到更底层的设备模块抽象:
int device_add(struct device *dev)
{struct device *parent = NULL;struct class_interface *class_intf;int error = -EINVAL;dev = get_device(dev);if (!dev)goto done;...if (dev->init_name) {dev_set_name(dev, "%s", dev->init_name);dev->init_name = NULL;}
...if (!dev_name(dev)) {error = -EINVAL;goto name_error;}
...parent = get_device(dev->parent);setup_parent(dev, parent);/* use parent numa_node */if (parent)set_dev_node(dev, dev_to_node(parent));/* first, register with generic layer. *//* we require the name to be set before, and pass NULL */error = kobject_add(&dev->kobj, dev->kobj.parent, NULL);if (error)goto Error;/* notify platform of device entry */if (platform_notify)platform_notify(dev);error = device_create_file(dev, &uevent_attr);if (error)goto attrError;if (MAJOR(dev->devt)) {error = device_create_file(dev, &devt_attr);if (error)goto ueventattrError;error = device_create_sys_dev_entry(dev);if (error)goto devtattrError;devtmpfs_create_node(dev);}
...error = device_add_class_symlinks(dev);if (error)goto SymlinkError;error = device_add_attrs(dev);if (error)goto AttrsError;error = bus_add_device(dev);if (error)goto BusError;error = dpm_sysfs_add(dev);if (error)goto DPMError;device_pm_add(dev);bus_probe_device(dev);
...
}内容较多,主要是和底层 kobject,kset,parent,sys 等等相关操作,这里关心到 bus_add_device 函数,往期望的 bus 上增加一个 device,成功后,调用 bus_probe_device:
void bus_probe_device(struct device *dev)
{struct bus_type *bus = dev->bus;int ret;if (bus && bus->p->drivers_autoprobe) {ret = device_attach(dev);WARN_ON(ret < 0);}
}这里不用多说了吧,调用到了 device_attach,和上面的 <5.2、platform_driver_register 情况>一样,形成了匹配后,调用了 probe!!
总体的流程是:
platform_device_register -> platform_device_add
-> device_add
-> bus_probe_device
-> driver_attach -> __driver_attach
-> match ? (0 return 1 ->)
-> driver_probe_device (matched)
-> really_probe
-> probe
5.3、小结
所以,不管是先注册 platform_device 还是 platform_driver,只要匹配上了,都会去执行到 probe 函数,也就是驱动的初始化函数!
参考文献:
https://blog.csdn.net/Richard_LiuJH/article/details/45825333
https://blog.csdn.net/Richard_LiuJH/article/details/48245715
https://blog.csdn.net/Hansomewang/article/details/78969006
https://blog.csdn.net/fml1997/article/details/77622860
https://blog.csdn.net/thl789/article/details/6723350
